Understanding Mydriasis: Causes, Symptoms, & More!
Ever looked in the mirror and noticed your pupils are unusually large? Dilated pupils, also known as mydriasis, is a condition where the black center of your eye is larger than normal and it's more than just a fleeting change in response to light. It's a fascinating yet sometimes concerning phenomenon that warrants closer examination.
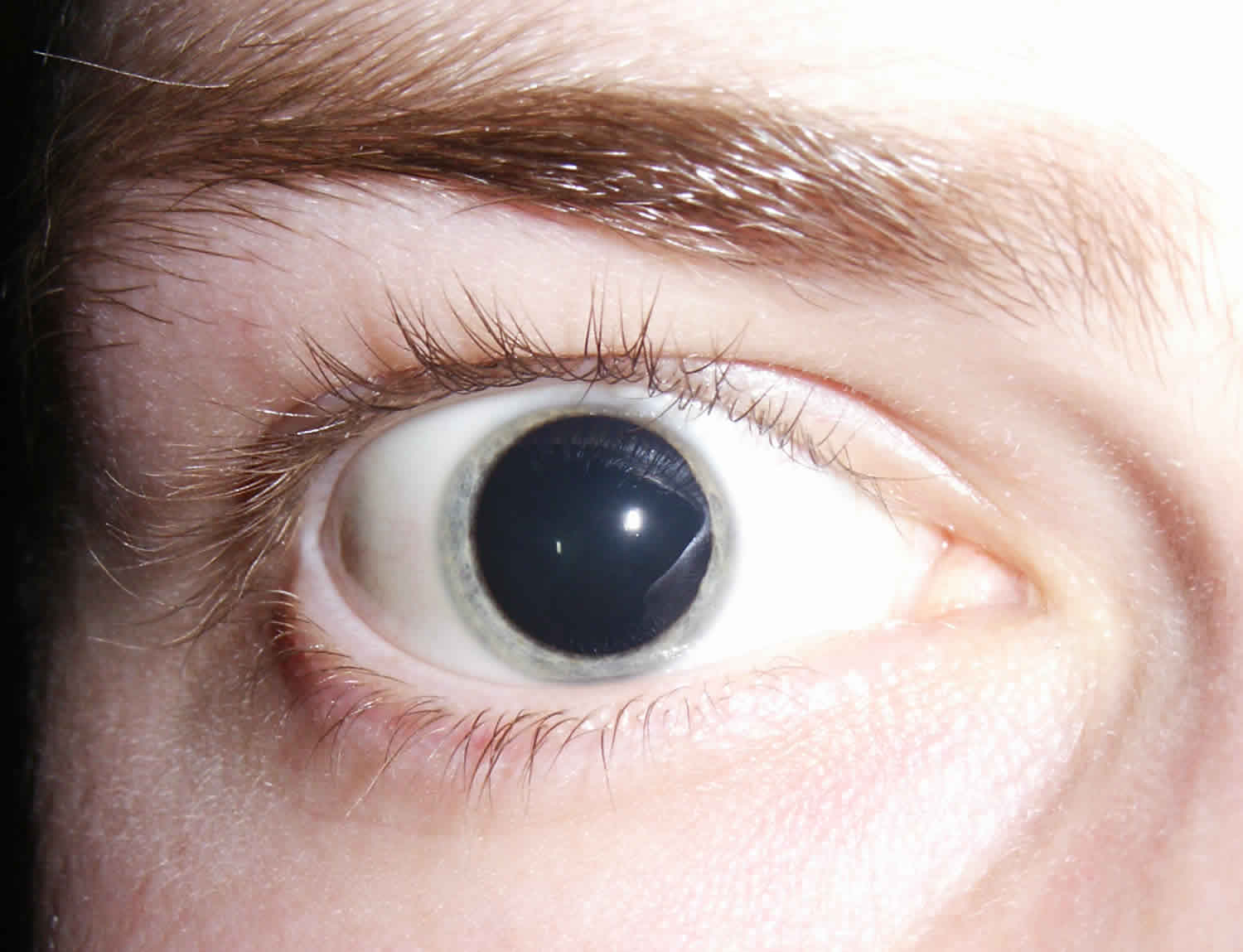
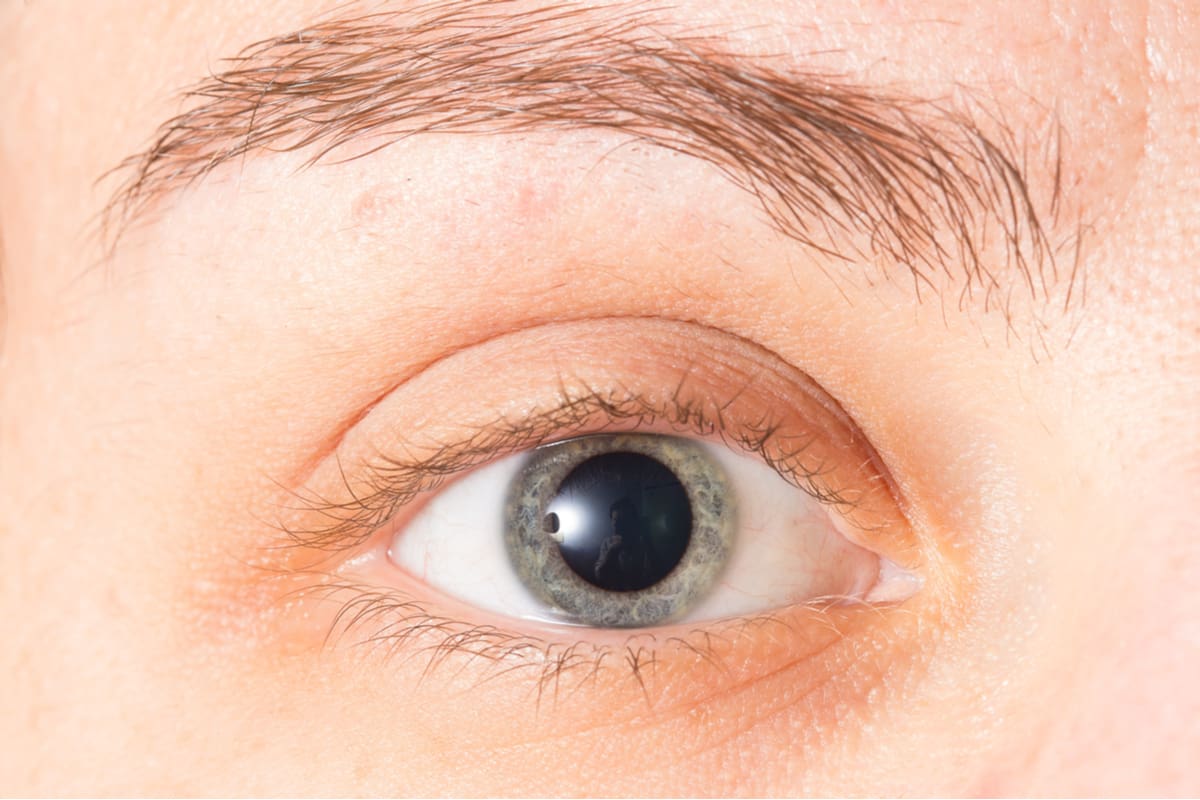
Mydriasis, at its core, is the enlargement of the pupil, the black opening in the center of the eye responsible for regulating the amount of light that enters. While pupils naturally dilate in dim environments to allow more light in, facilitating better vision in low-light conditions, mydriasis refers to dilation that occurs independent of these environmental changes. This can manifest in one or both eyes and can persist for varying durations.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Mydriasis: Abnormal dilation of the pupil beyond its normal range. |
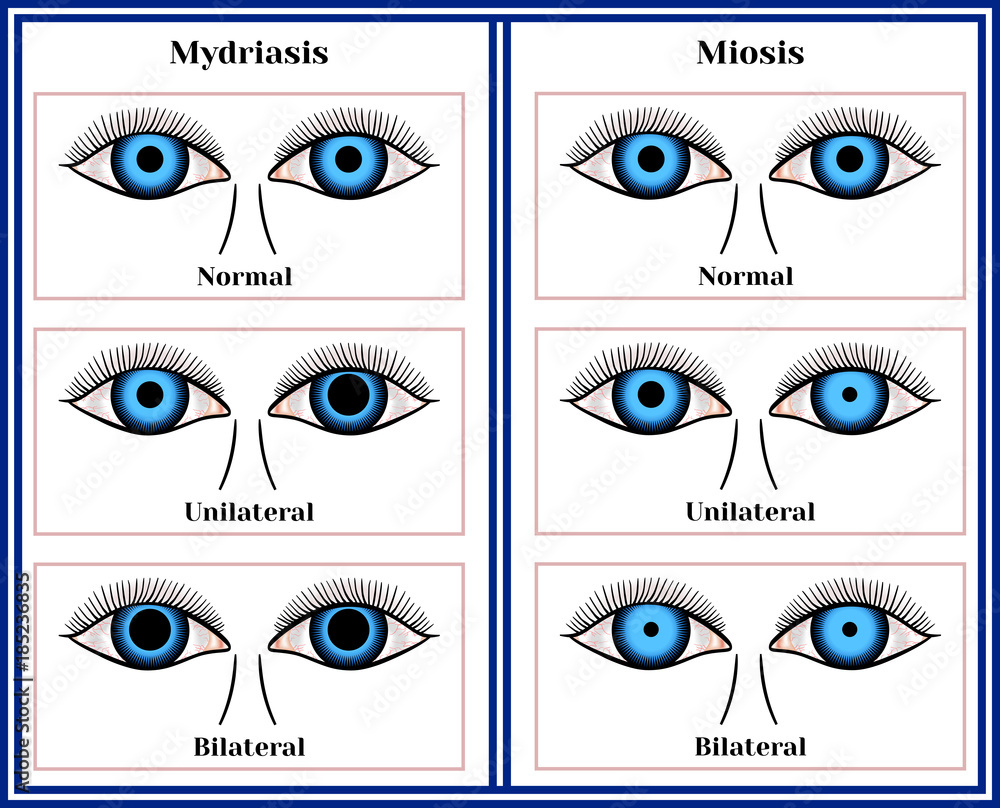
| Normal Pupil Function | Pupils constrict in bright light (miosis) and dilate in dim light to regulate light entry. |
| Causes |
|
| Symptoms |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Treatment | Treatment depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, no treatment is needed; in others, addressing the underlying medical condition is necessary. |
| Risk Factors |
|
| Complications | Angle-closure glaucoma, vision disturbances. |
| Traumatic Mydriasis | Mydriasis resulting from direct injury to the eye or head trauma. |
| Pharmacologic Mydriasis | Pupil dilation caused by topical agents or systemic medications. |
| Reference Website | American Academy of Ophthalmology |
Several factors can trigger mydriasis, ranging from routine medical procedures to underlying health conditions. One common cause is the use of dilating eye drops during eye exams. These drops temporarily paralyze the muscles that control pupil constriction, allowing the ophthalmologist to get a better view of the retina and other internal structures of the eye. The effects of these drops usually wear off within a few hours.
Certain medications can also induce mydriasis as a side effect. Anticholinergics, antihistamines, and antidepressants are among the drugs that can interfere with the normal pupillary response. Illicit drug use, particularly stimulants like cocaine and amphetamines, and hallucinogens, are also known to cause pupil dilation. Traumatic brain injury, stroke, or the presence of a tumor can exert pressure on the iris muscles, disrupting their ability to control pupil size, resulting in mydriasis in one or both eyes.
Beyond the physical causes, psychological factors can also contribute to mydriasis. Intense emotional states, such as fear, anxiety, or excitement, can trigger the release of adrenaline, a hormone that stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, leading to pupil dilation. This is why you might notice your pupils widening when you're feeling particularly stressed or surprised.
The implications of mydriasis vary depending on the underlying cause. In many cases, it's a temporary and harmless condition that resolves on its own. However, persistent or unexplained mydriasis can be a sign of a more serious medical problem. It's particularly concerning in individuals with narrow angles between the iris and cornea, as it can increase the risk of angle-closure glaucoma, a condition that can lead to vision loss if left untreated.
- Desiremovies More Explore Titles Movie Experiences Now
- Movierulz No Results What You Need To Know Safe Alternatives
One of the hallmark symptoms of mydriasis is, of course, enlarged pupils. This can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as sensitivity to light (photophobia), blurred vision, and headache. The severity of these symptoms can vary depending on the degree of pupil dilation and the underlying cause.
Diagnosing mydriasis typically involves a thorough eye examination by an ophthalmologist. The doctor will assess the size and reactivity of your pupils, as well as examine the internal structures of your eyes. If a head injury or neurological condition is suspected, a neurological examination may be necessary. The doctor will also inquire about your medical history, medications, and drug use to help determine the underlying cause of the mydriasis.
The treatment for mydriasis depends on the underlying cause. In many cases, no treatment is necessary, as the condition resolves on its own once the causative factor is removed. For example, if mydriasis is caused by dilating eye drops, the pupils will return to their normal size once the effects of the drops wear off. If mydriasis is a side effect of a medication, your doctor may recommend adjusting the dosage or switching to a different medication. In cases where mydriasis is caused by a more serious medical condition, such as a brain tumor, treatment will focus on addressing the underlying condition.
Mydriasis can also be classified based on its origin. Traumatic mydriasis refers to pupil dilation resulting from direct injury to the eye or head trauma. Pharmacologic mydriasis, on the other hand, is pupil dilation caused by topical agents or systemic medications. Understanding the type of mydriasis can help guide diagnosis and treatment.
Specifically, pharmacologic dilation of the pupil is one of the myriad explanations for unilateral or bilateral pupillary dilation. It is typically characterized by poor or no pupillary constriction to light or near stimuli. This means that even when exposed to bright light, the pupils remain enlarged and do not constrict as they normally would. This lack of reactivity is a key indicator of pharmacologic mydriasis.
The case of traumatic mydriasis secondary to a sweetgum ball ocular injury highlights the potential for long-term visual consequences from seemingly minor trauma. In this particular case, the mydriasis and associated accommodative dysfunction persisted for eight years before resolving. This underscores the importance of prompt and thorough evaluation following any ocular injury.
For instance, consider the scenario where an individual experiences a blow to the head during a sports game. Following the injury, they notice that one of their pupils is significantly larger than the other and does not constrict in response to light. This could be a sign of traumatic mydriasis, indicating potential damage to the iris muscles or the nerves that control them. In such cases, immediate medical attention is crucial to assess the extent of the injury and prevent further complications.
Mydriasis is a risk factor for angle closure glaucoma in certain individuals. This is most commonly seen in those with "narrow angles," which refers to an unusually narrow angle between the outer edge of the iris and the cornea (the clear part of the eye that covers the front of the eye). In these individuals, mydriasis can cause the iris to block the flow of fluid from the eye, leading to a sudden increase in eye pressure and potentially causing irreversible vision loss.
When the pupils dilate without any change in light, this is called mydriasis. It occurs when the pupil remains dilated (widened) and doesn't respond to light changes in an environment. It can happen due to an injury, medications, or psychological factors. Als mydriasis bezeichnet man die weitstellung der pupille ber einen durchmesser von 5 mm hinaus. Sie ist das gegenteil der miosis. Die pupille ist die ffnung im zentrum der iris, durch deren weite der lichteinfall ins auge reguliert wird. Die pupillen verengen sich bei zunehmender helligkeit (miosis) und erweitern sich bei z.
Understanding the nuances of mydriasis is essential for both healthcare professionals and individuals alike. By recognizing the potential causes, symptoms, and implications of this condition, we can ensure prompt diagnosis and appropriate management, ultimately safeguarding vision and overall health. If you experience persistent or unexplained pupil dilation, it's always best to consult with an eye care professional for a comprehensive evaluation.
The diagnostic procedures encompass a range of treatment protocols and ongoing monitoring strategies to effectively manage a broad spectrum of eye conditions.
What are ocular disorders that keep a large pupil from constricting? How does one test for pharmacologic mydriasis from topical agents?
- Vegamovies Netflix Seamless Access Guide 2024 Tips
- Beware Movierulz Kannada 2025 Download Is It Safe
Mydriasis, mydriatic pupil causes, diagnosis & treatment
Mydriasis (Pupil Dilation) Causes, Treatment and More MyVision
Miosis And Mydriasis