Unlock Google Search Secrets: Mastering The 'inurl:' Operator
Ever feel like the internet is a vast, untamed wilderness, teeming with information you can't quite grasp? The key to unlocking the internet's secrets lies in mastering the art of precise searching, and Google's search operators are your map and compass. They are the hidden levers that transform a frustrating search into a laser-focused quest for exactly what you need.
Among these powerful tools, the 'inurl:' operator stands out as a particularly effective method for pinpointing content. It allows you to specify keywords that must appear within the URL of a webpage, drastically narrowing your search and revealing pages that are highly relevant to your query. Whether you're a seasoned SEO professional, a curious researcher, or simply someone trying to find a specific piece of information, understanding how to wield the 'inurl:' operator can save you time and unlock a wealth of knowledge hidden beneath the surface of the web.
| Field | Information |
|---|---|
| Operator Name | inurl: |
| Function | Searches for keywords within the URL of a webpage. |
| Basic Structure | inurl:[keyword(s)] |
| Example Use Case | Finding blog posts about SEO: inurl:blog seo tips |
| Benefit | Provides a strong clue about the content's focus based on the URL's structure. |
| Advanced Use | Combining with other operators (e.g., site:) to refine search results. |
| Potential Applications | SEO research, competitor analysis, identifying specific types of web pages, vulnerability assessment. |
| Related Operators | intitle:, site:, filetype:, intext: |
| Caution | Over-reliance on inurl: may miss relevant pages where the URL doesn't explicitly contain the keywords. |
| Reference Link | Ahrefs - Google search operators |
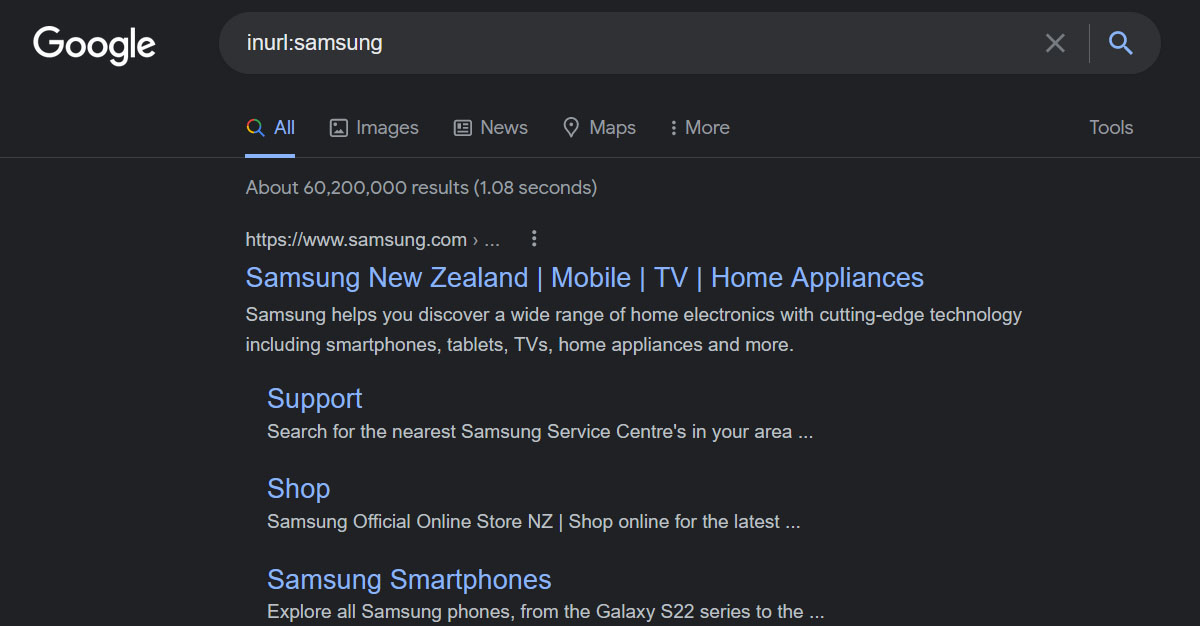
The beauty of the 'inurl:' operator lies in its simplicity. The basic structure is straightforward: you type 'inurl:' followed by the specific term or keyword you're targeting. For instance, a search for 'inurl:blogging tips' will direct the search engine to find URLs containing the term "blogging tips," providing insights into web pages focused on that very topic. This is particularly useful when the URL itself provides a strong indication of the page's content.
- Stream Download Your Guide To New Hindi Bollywood Movies
- Movierulz Is Free Movie Streaming Worth The Risk Years Insights
Think of it this way: many websites structure their URLs to reflect the content of the page. A blog post might have a URL like 'www.example.com/blog/seo-guide,' while a product page might have a URL like 'www.example.com/products/organic-shampoo.' By using the 'inurl:' operator, you're essentially telling Google to prioritize pages where the keywords are prominently displayed in this navigational structure. This is especially helpful for identifying specific types of content, such as blog posts, product pages, or even administrative login pages.
However, the 'inurl:' operator is not without its nuances. It's important to remember that it searches for the specified text anywhere within the URL, including folder names, file names, and subdomains. This can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. On one hand, it allows for a broad search, capturing pages where the keyword appears in any part of the URL. On the other hand, it can sometimes lead to irrelevant results if the keyword appears in an unexpected place within the URL.
So, why would you use 'inurl:' instead of simply searching for the keywords in the main search box? The key difference lies in the level of specificity. A regular search looks for the keywords anywhere on the page, while 'inurl:' specifically targets the URL. This makes 'inurl:' a more precise tool for finding pages that are highly focused on the specified keywords. For example, searching for "SEO tips" will return pages that mention SEO tips somewhere in the content, while searching for 'inurl:seo tips' will return pages where the URL itself contains the words "seo" and "tips," suggesting a more direct focus on that topic.
- Kannada Films 2024 Top Grossing Movies You Cant Miss
- Movierulz Tamil Cinema News Reviews More Updated
Furthermore, the 'inurl:' operator can be combined with other Google search operators to further refine your search. For example, you can use the 'site:' operator to limit your search to a specific website or domain. A query like 'site:whitehouse.gov inurl:policy' will search for pages on the White House website that have the word "policy" in their URL. This can be incredibly useful for researching specific topics on specific websites.
Beyond research and general information gathering, the 'inurl:' operator also has practical applications in the fields of SEO and cybersecurity. SEO professionals can use it to identify competitors who are targeting specific keywords in their URLs, providing insights into their SEO strategies. Cybersecurity professionals can use it to identify potential vulnerabilities by searching for specific file names or administrative pages in URLs. For instance, a search for 'inurl:admin' might reveal administrative login pages that could be vulnerable to attack.
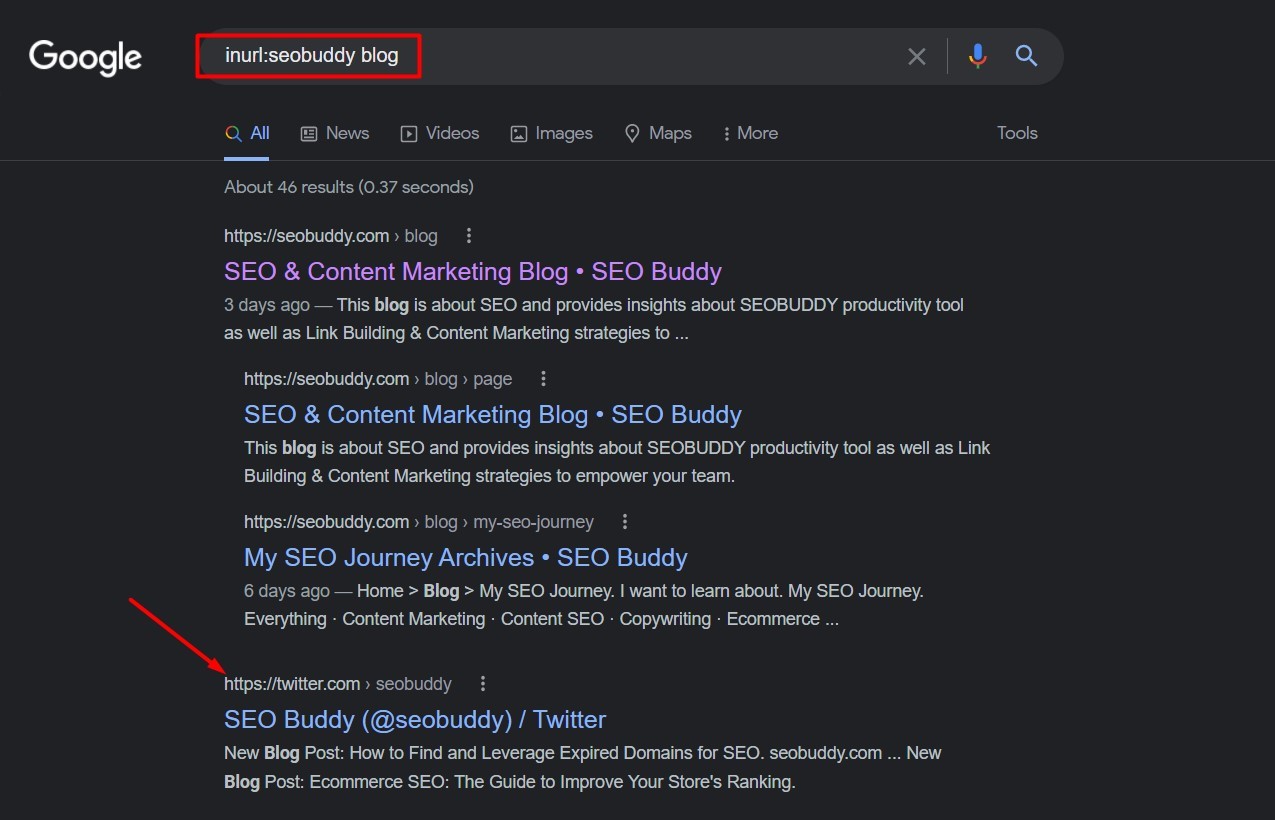
Let's delve into some specific examples to illustrate the power of the 'inurl:' operator. Imagine you're a blogger looking for collaboration opportunities with other SEO bloggers. You could use the query 'inurl:blog seo' to find blogs that have the words "blog" and "seo" in their URLs, indicating a focus on search engine optimization. This would provide a targeted list of potential collaborators.
Another example: let's say you're trying to find pages about a specific product, such as organic shampoo. You could use the query 'inurl:shampoo' to find pages that have the word "shampoo" in their URLs. This would likely return product pages, blog posts about shampoo, and other related content, all of which are highly relevant to your search.
Furthermore, consider the scenario of diagnosing indexing issues on your own website. If you're using tags for your blog posts and want to check if Google is indexing them properly, you could use the query 'inurl:tag' to identify indexed blog tag pages. This can help you identify any issues with your website's structure or indexing process.
It's also worth noting that the 'inurl:' operator is not case-sensitive. This means that 'inurl:blog' is the same as 'inurl:Blog' or 'inurl:BLOG.' This makes it easier to use, as you don't have to worry about capitalization errors.
However, there are some limitations to keep in mind. The 'inurl:' operator only searches for the specified keywords within the URL. It doesn't take into account the content of the page itself. This means that a page could have the word "blog" in its URL but not actually be a blog post. Therefore, it's important to use the 'inurl:' operator in conjunction with other search operators to get the most accurate results.
For example, you could use the 'intext:' operator to search for keywords within the content of the page. A query like 'inurl:blog intext:seo' would search for pages that have the word "blog" in their URL and also mention the word "seo" in their content. This would provide a more targeted list of blog posts about search engine optimization.
Another useful operator is the 'intitle:' operator, which searches for keywords in the title of the page. A query like 'inurl:blog intitle:seo' would search for pages that have the word "blog" in their URL and also have the word "seo" in their title. This would further refine your search and provide even more relevant results.
In addition to these basic operators, there are also several advanced search operators that can be used in conjunction with 'inurl:' to achieve even more precise results. For example, the 'filetype:' operator allows you to search for specific file types, such as PDFs or DOCs. A query like 'inurl:report filetype:pdf' would search for PDF files that have the word "report" in their URL. This can be useful for finding specific documents or reports.
Similarly, the 'daterange:' operator allows you to search for pages that were published within a specific date range. A query like 'inurl:news daterange:2458849-2458856' would search for pages that have the word "news" in their URL and were published within the specified date range. This can be useful for finding recent news articles on a particular topic.
The minus operator (-) allows you to exclude certain terms from your search. For example, if you were searching for information about Jaguar cars but didn't want to see results about the Jaguar animal, you could search for: jaguar -animal. This can be useful for filtering out irrelevant results and focusing on the information you're actually looking for.
Using these combinations, you can begin to see how powerful and versatile Google's search operators can be. Don't be afraid to experiment and find new ways to combine operators to achieve your specific search goals. The possibilities are virtually endless.
Beyond the legal and ethical uses, the 'inurl:' operator can also be misused for malicious purposes. Hackers can use it to find vulnerable targets by searching for specific file names or administrative pages in URLs. For example, a search for 'inurl:index.of' can reveal websites that have directory listing enabled, which can expose sensitive files and information. This highlights the importance of securing your website and protecting it from potential attacks.
In conclusion, the 'inurl:' operator is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance your Google searching abilities. By understanding how it works and how to combine it with other operators, you can unlock a wealth of information hidden beneath the surface of the web. Whether you're a researcher, an SEO professional, or simply someone trying to find a specific piece of information, mastering the 'inurl:' operator will undoubtedly save you time and improve your search results. Always remember to use this power responsibly and ethically.
The examples presented here offer a solid foundation for using Google's search operators. However, the true potential lies in your own experimentation and creativity. Don't hesitate to mix and match these operators, explore their nuances, and discover new ways to use them that perfectly suit your needs. The more you practice, the more proficient you'll become at harnessing the power of Google search.
So, are you ready to unlock the internet's secrets? Start experimenting with the 'inurl:' operator and discover the power of precise searching. The possibilities are endless, and the rewards are well worth the effort. Happy searching!
- Movierulz No Results What You Need To Know Safe Alternatives
- Bolly4u Legal Streaming Watch Bollywood Movies Online Year
Understanding the Power of the Google inURL Search Operator
Inurl Explained How To Use Search Operators vrogue.co
Inurl Explained How To Use Search Operators vrogue.co